RVP Vs TVP of Gasoline
Is Reid Vapor pressure of gasoline (RVP) is same as true vapor pressure (TVP) ?
What is difference between RVP and TVP value ?
The blog article explain difference between RVP and TVP at slight higher technical level than common man perspectives.
List of all blog articles on Petroleum QC by RJ Patel.
Reid vapor pressure is a common measure of the volatility of gasoline. It is defined as the absolute vapor pressure exerted by a liquid at 37.8 °C (100 °F) as determined by the test method ASTM-D-323. The test method measures the vapor pressure of gasoline, volatile crude oil, and other volatile petroleum products, except for liquefied petroleum gases. RVP is stated in kilopascals and represents a relative pressure to the atmospheric pressure because ASTM-D-323 measures the gauge pressure of the sample in a non-evacuated chamber. All values are in SI units and are regarded as standards. Imperial units are for information only.
Lists of Android/iOs Apps developed on Petroleum Calculation - see here. (These apps convert Density/API gravity exactly as per ASTM tables 5a, 5b, 6a, 6b, 23a,23b, 24a,24b, 53a,53b, 54a,54b to standard temperature 15 C, 20 C and 60 F.)
The matter of vapor pressure is important relating to the function and operation of gasoline-powered, especially carbureted, vehicles. High levels of vaporization are desirable for winter starting and operation and lower levels are desirable in avoiding vapor lock during summer heat. Fuel cannot be pumped when there is vapor in the fuel line (summer) and winter starting will be more difficult when liquid gasoline in the combustion chambers has not vaporized. Thus, oil refineries manipulate the Reid Vapor Pressure seasonally specifically to maintain gasoline engine reliability.
The Reid vapor pressure (RVP) differs slightly from the true vapor pressure of a liquid due to small sample vaporization and the presence of water vapor and air in the confined space of the test equipment. That is, the RVP is the absolute vapor pressure and the TVP is the partial vapor pressure.
TVP is the actual vapor pressure of a liquid product at a specified temperature and is measured with a sample cylinder.
Thus, RVP is a measured value at 37.8 Deg C where as vapor pressure at any other temperature can be more at higher temperature and lower at lower temperature than 37.8 deg C for same gasoline.
Typically for Gasoline, approx relationship between RVP and TVP at 37.8 deg C are tabulated for few gasoline samples.
TVP is the actual vapor pressure of a liquid product at a specified temperature and is measured with a sample cylinder.
Thus, RVP is a measured value at 37.8 Deg C where as vapor pressure at any other temperature can be more at higher temperature and lower at lower temperature than 37.8 deg C for same gasoline.
Typically for Gasoline, approx relationship between RVP and TVP at 37.8 deg C are tabulated for few gasoline samples.
RVP
At 37.8 C
|
TVP
At 37.8 C
|
psi
|
psia
|
5
|
5.8
|
6
|
6.8
|
7
|
7.9
|
8
|
8.9
|
9
|
9.9
|
10
|
11
|
11
|
12
|
12
|
13.1
|
13
|
14.1
|
14
|
15.2
|
15
|
16.2
|
The tabulated values can be expressed in equation: RVP = 0.959*TVP - 0.539
RVP And TVP both at 37.8 deg C.
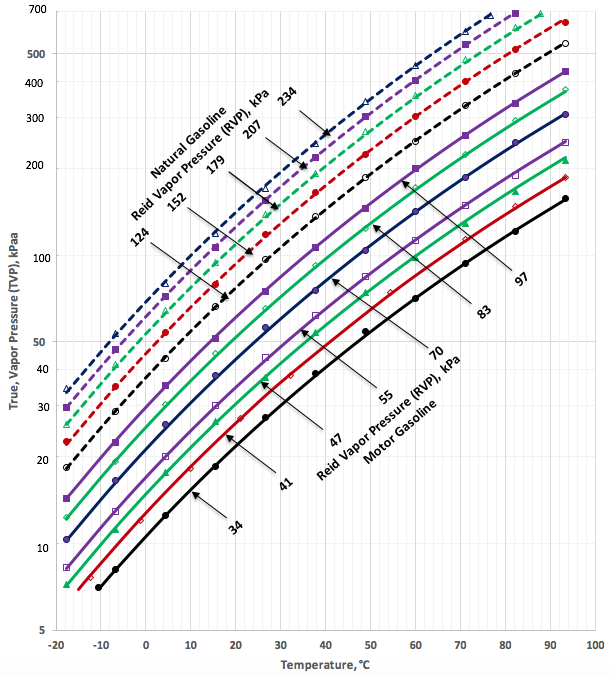
At different temperatures relationship fo Gasoline is expressed in a graph at reference:
http://www.jmcampbell.com/tip-of-the-month/2016/02/correlations-for-conversion-between-true-and-reid-vapor-pressures-tvp-and-rvp/
Author of this reference is Dr. Mahmood Moshfeghian
Author of this reference is Dr. Mahmood Moshfeghian
Follow me on twitter @RJPatel13 to get notification when my new post is available in my blog.
Comments