Naphtha and its Aromatics Content
Naphtha and its Aromatics Content
The article details significance of aromatics content in naphtha
and leads to use of Aniline to different dimple test methods, not only for
aromatics but also naphthenes and paraffins in naphtha.
Naphtha
Naphtha is a lighter cut of petroleum usually boiling range
anywhere between 30 to 2000C. Naphtha is a general term as each
refinery produces its own naphtha with its own unique initial and
final boiling points and other physical and compositional characteristics.
Naphtha like any petroleum products consist mainly four
hydrocarbon groups namely Paraffins, Olefins, Naphthenes and Aromatics
popularly expressed as PONA.
Further it’s specific boiling range cuts are used for different
purpose in various industries as solvents to dissolve other substances, besides
a large quantity is used as starting feedstock in many industrial
applications such as raw material for plastics such as polypropylene and
polyethylene etc. For production of hydrogen and ammonia in fertiliser
industry specific quality naphtha is required.
Straight run naphtha from atmospheric distillation units do not
contain Olefins.
Some refinery naphthas also contain olefinic hydrocarbons such as
derived from the fluid catalytic cracking, visbreaker and/or cocking processes
used in many refineries. Those olefins containg naphthas are often referred as “cracked
naphtha”.
Aromatics in naphtha
Aromatics in naphtha particularly find itself of more interest
among its users in industry since the yield of the desired end product
depends upon the composition or percentage of aromatics in naphtha. Therefore,
oil industry produces various grade of naphtha named as low Aromatic Naphtha
(LAN), high Aromatic Naphtha (HAN) etc. Its specification limits aromatics as
required by specific industry and contracted with Refinery like Aromatics max
5%v, max 20%v, min 10% etc.
In view of above, different grades of naphthas are produced,
stored and transported to various industries where personnel involved in
handling the product gives important to “Aromatic Content” in naphtha.
Author has done a considerable research in the field of quality of
naphtha and have formulated significantly useful test methods and empirical
relationship equations to determine aromatics content quantitatively in naphtha,
the methods are simple, quick and can be performed by non-technical personnel,
without needing the lengthy-time consuming, sophisticated laboratory
equipment.
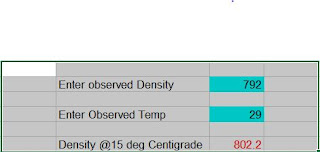
Following links leads to some of the methods derived using Aniline concepts:
Comments